Problem
Question
You are given a positive integer
k. You are also given: 1) a 2D integer arrayrowConditionsof sizenwhererowConditions[i] = [abovei, belowi], and 2) a 2D integer arraycolConditionsof sizemwherecolConditions[i] = [lefti, righti].
The two arrays contain integers from 1 to k.
You have to build a k x k matrix that contains each of the numbers from 1 to k exactly once. The remaining cells should have the value 0.
The matrix should also satisfy the following conditions:
- The number
aboveishould appear in a row that is strictly above the row at which the numberbelowiappears for allifrom0ton - 1. - The number
leftishould appear in a column that is strictly left of the column at which the numberrightiappears for allifrom0tom - 1.
Return any matrix that satisfies the conditions. If no answer exists, return an empty matrix.
Example 1:
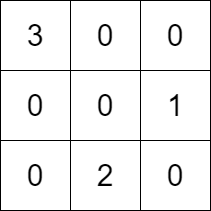
Input: k = 3, rowConditions = , colConditions = Output: Explanation: The diagram above shows a valid example of a matrix that satisfies all the conditions. The row conditions are the following:
- Number 1 is in row 1, and number 2 is in row 2, so 1 is above 2 in the matrix.
- Number 3 is in row 0, and number 2 is in row 2, so 3 is above 2 in the matrix. The column conditions are the following:
- Number 2 is in column 1, and number 1 is in column 2, so 2 is left of 1 in the matrix.
- Number 3 is in column 0, and number 2 is in column 1, so 3 is left of 2 in the matrix. Note that there may be multiple correct answers.
Example 2:
Input: k = 3, rowConditions = , colConditions = Output: Explanation: From the first two conditions, 3 has to be below 1 but the third conditions needs 3 to be above 1 to be satisfied. No matrix can satisfy all the conditions, so we return the empty matrix.
Solutions
🏆 Topological Sorting
Time Complexity: | Space Complexity:
To solve the problem, we need to utilize a technique called topological sorting.
Topological sorting is an excellent method for handling priorities and dependencies. Imagine you are organizing a set of tasks where some tasks must be completed before others. For example, you can’t bake a cake until you’ve mixed the ingredients. If we represent each task as a number and each dependency (must-do-before) as a directed arrow from one task to another, we can use topological sorting to find an order to complete the tasks without violating any dependencies.
In simple terms, we build a graph that represents dependencies.
The problem can be divided into two subproblems:
- What is the vertical sequence of all numbers?
- What is the horizontal sequence of all numbers?
Once we solve these problems, constructing the matrix becomes straightforward.
Let’s consider only the horizontal sequences. In the first example, we know that:
- 2 should be before 1
(2 -> 1) - 3 should be before 2
(3 -> 2)
Combining these conditions, we get:
3 -> 2 -> 1
How do we know if it is impossible to build the matrix with the given conditions? It’s very simple - if there is a loop in the graph. For example, if we add the condition:
- 1 should be before 3
Then we have:
3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3
This forms a loop, making it impossible to build the matrix as per the given conditions.
class Solution:
def buildMatrix(self, k: int, rowConditions: List[List[int]], colConditions: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
##############################################
# TOPOLOGICAL SEARCH (dfs & main method) #
##############################################
def dfs(graph, src, visited, path, order):
if src in path:
return False
if src in visited:
return True
visited.add(src)
path.add(src)
for dst in graph[src]:
if not dfs(graph, dst, visited, path, order):
return False
order.append(src)
path.remove(src)
return True
def topo_sort(edges):
graph = defaultdict(list)
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
visited, path = set(), set()
order = []
for src in range(1, k + 1):
if src not in visited:
if not dfs(graph, src, visited, path, order):
return []
return order[::-1]
##############################################
##############################################
##############################################
row_order = topo_sort(rowConditions)
col_order = topo_sort(colConditions)
if not row_order or not col_order:
return []
val_to_row = {num: i for i, num in enumerate(row_order)}
val_to_col = {num: i for i, num in enumerate(col_order)}
result = [[0] * k for _ in range(k)]
for num in range(1, k + 1):
row, col = val_to_row[num], val_to_col[num]
result[row][col] = num
return result